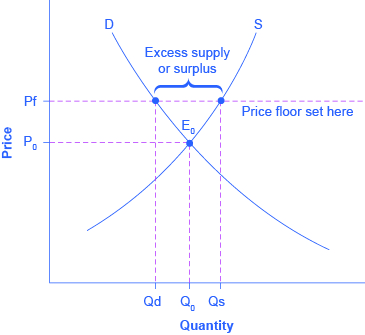
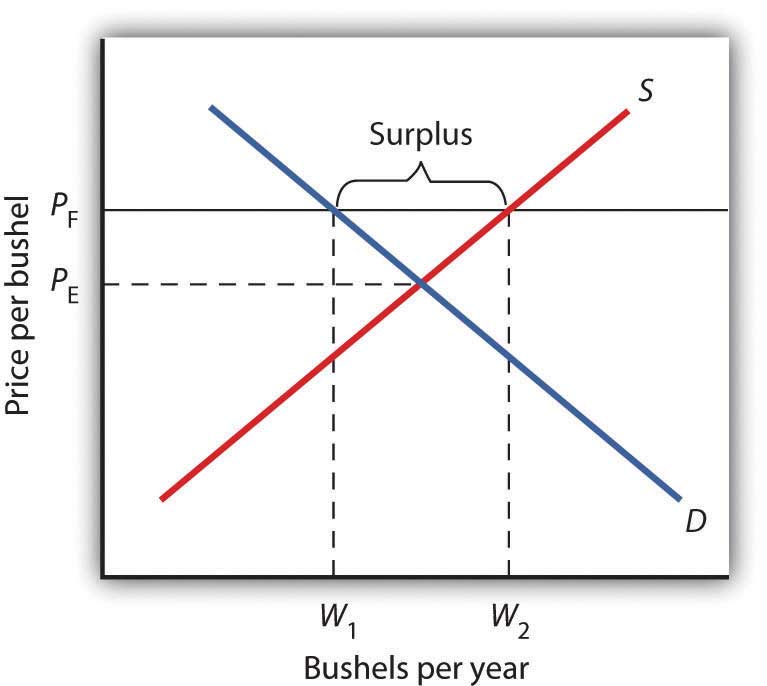
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
Do binding price floors create surpluses.
How price controls reallocate surplus.
Surpluses d wasteful increases in quality.
Last month i discussed the distorting effects of government imposed price ceilings.
Minimum wage and price floors.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.
Setting binding price floors.
Legislating a minimum wage creates unemployment tuesday december 1 1998.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
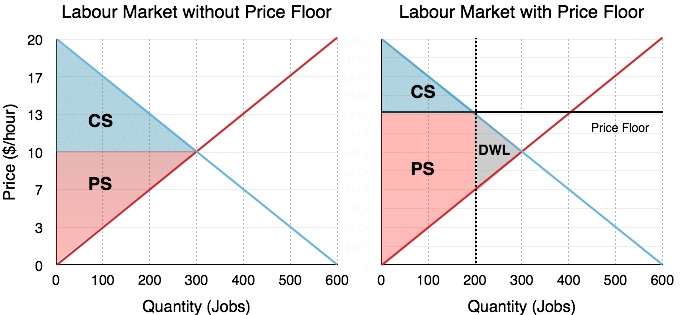
When a binding price floor is used it will create a deadweight loss if the market was efficient before the price floor introduction.
They are generally used to increase prices such as wages but are only effective binding when placed above the market price.
Not content to limit the disruptive impact on economic.
D maximum gains from trade.
A price floor is an established lower boundary on the price of a commodity in the market.
Price floors are a common government policy to manipulate the market.
This has the effect of binding that good s market.
Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers.
Binding price ceilings would create all of the following effects except.
A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Types of price floors.
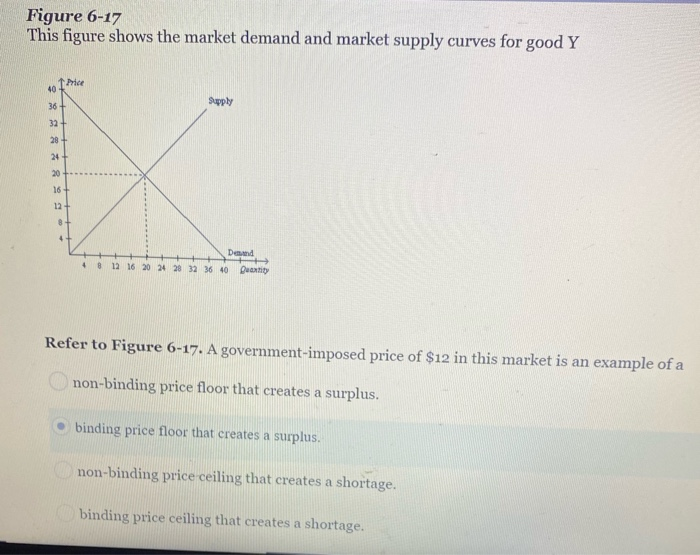
A binding price floor causes.
Price floors surpluses and the minimum wage.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
Price ceilings and price floors.
This is the currently selected item.
Price and quantity controls.
B reductions in product quality.
C a misallocation of resources.
Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low.
The most common price floor is the minimum wage the minimum price that can be payed for labor.
Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity.
Governments can set prices on certain goods artificially high and create economic disequilibrium and binding price floors on these goods through the laws they enact.
Economics labor unions demand supply and demand minimum wage price.